3 Aspects of CNC Machining Parts That You Should Know
Curious what aspects of CNC Machining you need to know? Consider this.
According to Foreign Policyi.org:
“'Custom made CNC machining parts involving a variety of plastic and metal materials, quick prototyping or end-user applications, both CNC milling and turning for mirror-like surface finishing and uphold tight tolerance.'
1. What is CNC Machining?
"CNC machining refers to a manufacturing process to fabricate simple as well as complex CNC machining parts with miniature dimensions by utilizing pre-programmed computer software. The acronym CNC stands for “Computer Numerical Control” and it is basically a subtractive manufacturing process which removes layers of materials from a workpiece by the numerically controlled program.
"Due to its compatibility with a wide variety of materials, CNC machining parts can be made of metals, plastics, wood, glass, foam, composites, and so on. It is an autonomous process that does not require human intervention, thus, it is more accurate, specific, cheap labor cost, and less time-consuming. It is the opposite of the additive manufacturing process (like 3D printing) or mass-replication technique (like injection molding) since it is a subtractive manufacturing method.
2. CNC Machining Material Considerations
"The most important feature which enables them to stand out from its competitors is their suitability to a variety of engineering materials including both plastic (PEEK, PC, PE, PTFE, nylon, etc.) and metal (brass, steel, aluminum, etc.).
Plastic:
"Engineering plastics or polymers are popular because of their high strength, resilience, toughness, lack of conductivity, resistance to corrosion, color, processing, transparency, and low cost. To manufacture high precision plastic parts, CNC machining of plastics is a very strong candidate. It is the most widespread method to manufacture plastic parts with strict tolerance limits and excellent surface finish. Unlike the injection molding process, in plastic CNC machining, molds are not required, hence it moderates the costs and startup times.
"CNC machining of plastics is similar to machining metals however, it requires different cutting speeds, cutting tools, and tool compensation to attain desired surface roughness and tolerances. CNC machined plastics have widespread applications including plastic medical components. Generally, in biomedical devices, they require high precision and geometry. Some examples of such medical devices include anesthetic and therapy components, surgical and dental instruments, catheters, diagnostic devices, cardiac implants, orthopedic, and other implantable devices.
Metals:
"Properties of metals are different than those of plastics; they are heavy due to the densely packed structure. Metals can outclass almost all material groups in some specific applications where thinness is critical. CNC machining of metals can provide us tight tolerance, mirror-like surface finish, and complex size and shape. You can get your functional metal parts as quickly as one working day by CNC machining services. The precision offered by CNC machining is the best choice for prototyping and rapid production of small and large metal parts. Among the wide variety of metal materials which are compatible with CNC machining services, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Brass, Copper, Magnesium, Steel Alloy, and Titanium are most popular and most widely used.
CNC milling parts
"The most commonly used method to fabricate almost 80% of the plastic parts is the milling parts. However, it is not only limited to plastic products but also used widely for manufacturing metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, brass, titanium, and so on. It is a subtractive technique that removes plastic or metal from the workpiece by a numerically controlled program. Mostly, the milling machines are categorized by their number of axes. A standard CNC milling machine mostly has three axes X, Y, & Z however, to manufacture parts having complex shapes and size, there are now 5-axis, 6-axis milling machines.
"It is mostly used to fabricate any rotationally symmetrical shape by removing material from the workpiece very rapidly. Turned parts are often adorned with an excellent surface finishing and it often requires no post-processing.
"Typically, a lathe or turning machine is employed for CNC turning parts. It works in a linear motion by feeding the cutting tool along the surface of the rotating workpiece. In doing so, it removes material around the perimeter until the preferred diameter is attained. Some examples of turned parts are cylinder-shaped parts with external and internal structures. By the CNC turning method, almost all kinds of materials can be machined such as all types of steel, aluminum, cast iron, brass, copper, and bronze, along with plastics such as nylon, fiberglass, and PTFE.
3. Tips for Maintaining Tight Tolerances
"Another term to express machining tolerance is dimensional accuracy which implies an acceptable variance in a part or cutting tool. In order to obtain high performing parts with maximum quality, tight tolerances are very critical. Here are some tips for holding tight tolerances while manufacturing CNC machining parts:
To select the perfect tool:
"We have to be very cautious and wise with the choice of tools for tight tolerances. It is to be ensured that for exceptionally tight tolerances, a specific set of tools including separate ones for roughing and finishing should be used. Furthermore, good quality cutting tools can provide more precision than a dull or blunt head cutting tool.
Warm up the spindle:
"A routine warm-up is extremely important for A CNC machine to work at its maximum. It is advised to run the machine for around 15–20 minutes before starting the actual milling procedure. It allows parts of the machine to reach an ideal temperature and will help diminish the effects of thermal expansion during milling.
Effect of the temperature:
"For holding tight tolerances, thermal stabilization is one of the most important things. A slender deviation from the ideal temperature can largely influence the dimensions of the parts in various ways. Therefore, it should always be kept in mind to place the machine in a temperature-controlled environment.
Calibration of equipment:
"Apart from being extremely cautious on all the above points, a desired level accuracy or precision may not be achieved after the machine is used for a longer period of time. It’s time to calibrate the equipment. It is very natural for the machine to loosen up after being used for thousands of hours and it’s unavoidable. However, calibrating, servicing and annual maintenance can keep a fitted leash on the machine precision.
In Conclusion
"CNC machining of plastic and metal parts stands out from all other manufacturing processes available in the industry for its diversity, precision, and comparatively faster process. Almost any type of plastic or metal part can be fabricated by the CNC milling or turning process with strict tolerances if the machine is operated and maintained carefully."
Aerostar increases its Bench Strength to Help US companies Source from India


Aerostar increases its Bench Strength to Help US companies Source from India
Expanding their newest facility, Aerostar hires new processing engineer, Gopinath Chakkaravarthy, for CNC Manufacturing at its Bengaluru office in India. The position focuses on programming, an integral part of the manufacturing process that supports supply chain services for Aerostar’s US customers.
Gopinath Chakkaravarthy brings 16 years of CNC Programming experience including work for big name global industries along with strong team building skills to bring the best out of coworkers. Ready for a challenge, Chakkaravarthy is taking the lead as Aerostar’s Manufacturing Process Engineer through MasterCAM.
Aerostar is eager to welcome a programmer with such strong skills and experience to the team. Chakkaravarthy’s responsibilities include 3, 4, & 5 axis CNC mill programming for all machines located in the US and at suppliers worldwide, as well as specialty tool design, lathe programming for all machines. CNC cycle time estimation, fixture design and tool design. All programming will support Aerostar Manufacturing’s efforts in sourcing castings, forgings, precision machining and complex assemblies for exports to its US customer base.
With an eye on expanding its sourcing and supply chain, Aerostar will continue to grow its team in India to help US customers outsource machined parts and assemblies from India.
CNC MACHINE MARKET 2020 BOOMING WORLDWIDE
The CNC machine market is expected to continue to see growth in the coming years. Consider this analysis.
According to Cole Market Research:
"Global CNC Machine Market Research Report’, the report is complete with an elaborate research undertaken by prominent analysts and a detailed analysis of the global industry place. The study is inclusive of a well-elaborated, extensive scrutiny of this industry alongside major parameters that may most likely have an influence on the market commercialization matrix. A SWOT analysis can be quite handy when it comes to determining the drivers and restraints of the CNC Machine market. The CNC Machine report aims to underline all the key aspects of the CNC Machine market to keep you updated about the recent happenings of the market, for instance, key players and brand’s acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures, recent developments, products launches, and the competitive research. The competition is expected to intensify in the upcoming years and augment the need for proper strategizing for business players. The CNC Machine report further explains the market definition, classifications, applications, engagements, and global reach is for the CNC Machine industry while giving a CAGR forecast for the period of 2020 and 2027. Few of the major competitors currently working in the global CNC Machine market are AMADA MACHINE TOOLS CO., LTD.; Amera-Seiki Corporation; DMG MORI CO., LTD.; SCM Group; General Technology Group Dalian Machine Tool Corporation; DATRON; FANUC CORPORATION; Haas Automation, Inc – CNC Machine Tools; Hurco Companies, Inc.;
"Global CNC machine market is expected to rise to an estimated value of USD 113.54 billion by 2026, registering a substantial CAGR in the forecast period of 2019-2026. This rise in market value can be attributed to the growing demand for reducing the operational costs associated with the operational costs of the end-use manufacturing industries.
Global CNC Machine Market Dynamics:
Market Drivers:
"Rapid demand for effective machineries from industries that provide high levels of productivity with lower amount of down time
Surge in the availability of IoT technology, as well as machine learning resulting in the various beneficial features associated with the machines is expected to augment growth of the market
Growing demand for equipments and machineries that can handle mass-production at an effective and efficient scale is expected to drive the growth of the market
Market Restraints:
"Large costs associated with the purchasing of these machines as well as the costs associated with their maintenance; this factor is expected to restricts the growth of the market
Investments in the establishment of these machineries result in greater unemployment rate due to the lack of engineers and individuals required to operate these machineries also restricts the growth of the market
"Important Features of the Global CNC Machine Market Report:
1) What all companies are currently profiled in the report?
"List of players that are currently profiled in the report- Okuma Corporation; Yamazaki Mazak Corporation; Shenyang Machine Tools Co.,Ltd.; Ellison Technologies, Inc.; The Lincoln Electric Company; Fagor Automation; GSK CNC EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD.; HEIDENHAIN; Smiths Machine; MAG IAS GmbH; JTEKT Corporation; GF Machining Solutions Management SA; Hyundai WIA among others.
** List of companies mentioned may vary in the final report subject to Name Change / Merger etc.
2) What all regional segmentation covered? Can specific country of interest be added?
Currently, research report gives special attention and focus on following regions:
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific etc.
3) Can inclusion of additional Segmentation / Market breakdown is possible?
"Yes, inclusion of additional segmentation / Market breakdown is possible subject to data availability and difficulty of survey. However a detailed requirement needs to be shared with our research before giving final confirmation to client.
"Global CNC Machine Market Segmentation:
"By Type
"Lathe Machines
"Milling Machines
"Laser Machines
"Grinding Machines
"Welding Machines
"Winding Machines
"Others
"By Application
"Machinery Manufacturing
"Automobiles
"Electronics
"Healthcare
"Aerospace & Defense
"By End-Use
"Automotive
"Aerospace & Defense
"Construction Equipment
"Power & Energy
"Industrial
"Others
"Region wise analysis of the top producers and consumers, focus on product capacity, production, value, consumption, market share and growth opportunity in below mentioned key regions:
"North America – U.S., Canada, Mexico
"Europe : U.K, France, Italy, Germany, Russia, Spain, etc.
"Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, India, Southeast Asia etc.
"South America – Brazil, Argentina, etc.
"Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, African countries etc.
"Key Highlights from CNC Machine Market Study.
"Revenue and Sales Estimation — Historical Revenue and sales volume is presented and further data is triangulated with top-down and bottom-up approaches to forecast complete market size and to estimate forecast numbers for key regions covered in the report along with classified and well recognized Types and end-use industry. Additionally macroeconomic factor and regulatory policies are ascertained in CNC Machine industry evolution and predictive analysis.
"Manufacturing Analysis —the report is currently analyzed concerning various product type and application. The CNC Machine market provides a chapter highlighting manufacturing process analysis validated via primary information collected through Industry experts and Key officials of profiled companies.
"Competition — Leading players have been studied depending on their company profile, product portfolio, capacity, product/service price, sales, and cost/profit.
"Demand & Supply and Effectiveness — CNC Machine report additionally provides distribution, Production, Consumption & EXIM** (Export & Import). ** If applicable
"Key Highlights of Report
"Overview of key market forces propelling and restraining market growth
"Offers a clear understanding of the competitive landscape and key product segments
"An analysis of strategies of major competitors
"Detailed analyses of industry trends
"A well-defined technological growth map with an impact-analysis
"Provides profiles of major competitors of the market.
"Details of their operations, product and services.
"Recent developments and key financial metrics."
July Survey Finds CEO Optimism On Economy Nearing Pre-Crisis Levels
For some CEOs, the outlook on the economy is nearing pre-crisis levels which could mean positive change for the end of 2020.
According to Melanie C. Nolen with Chief Executive:
"Chief Executive’s July polling of 326 U.S. CEOs finds confidence in business conditions a year from now continuing an upward climb from the Covid-created trough in May. At 6.6 out of 10 on our 1-10 scale, CEO confidence is now nearing the level it was in January (6.7), just before the crisis struck.
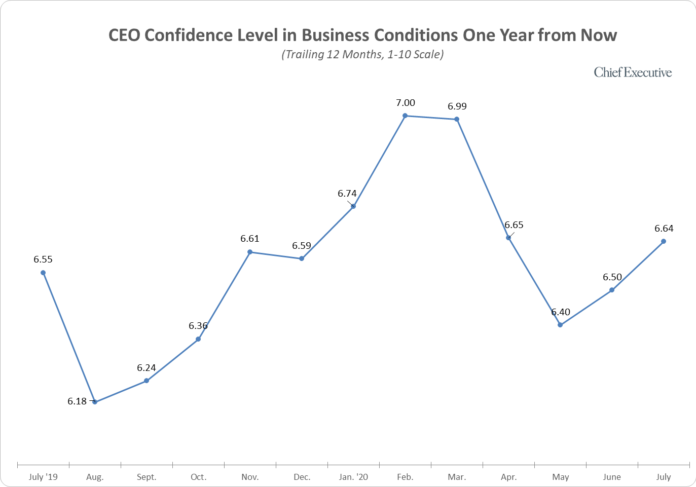
"Confidence in the current economic environment is also rising, adding 13 percent to last month’s gains, although it remains 26 percent below its January level, at 5.2 out of 10.

"CEOs who are optimistic about the future say they are betting on a Covid recovery, via vaccine or treatment. But many say positive news about the virus could be offset by the outcome of the federal election in November—although opinions on what outcome they’d prefer were fairly evenly split among those who expressed an opinion.
“'With any luck, the nation will have different leadership, the virus will be better controlled, and businesses will have incentives to modify their operations to adapt,' said Peter Altschuler, president of Wordsworth & Company, explaining his forecast for an improved economic environment next year.
“'More people should be back to work a year from now, as I have optimism for a vaccine or at least some immunity to the Covid virus to allow business to get back to normal,' said Jim Nelson, president of Parr Instrument Company.
“'Surprised to see that the U.S bankruptcy filings have not been so bad. The pessimistic forecasts were too dire,' said Scott Heim, president of manufacturer Evo America. 'American consumers are ready to get back out to the restaurants and spend dollars.' For that reason, he anticipates future business conditions to be 'very good,' with an 8 out of 10.
“'I expected to have three months minimum of 50 percent down because of Covid,' said Diana Mini, president of Shark Industries. 'June was a huge month. I was only down one month at 50 percent, and we are only down about 3-4 percent for the whole year and business is very strong.'
"Jim Brewster, president of Venus Fashion, said that while he expects 'great economic turmoil in the rest of 2020,' he forecasts that 'by 1st quarter 2021, we will be able to figure out how to ‘live’ with the virus (regardless of vaccine development).' For that reason, he rates conditions a year from now as 'good' with a 6 out of 10.
Improving Outlooks For Profits, Capex, Hiring
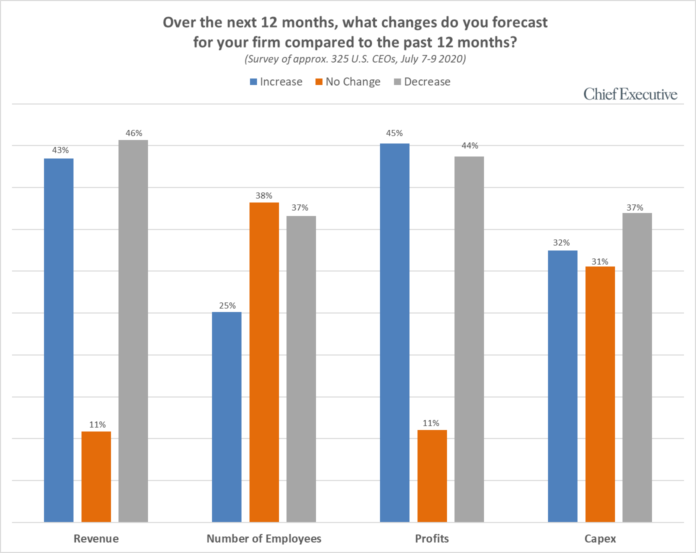
"The rising optimism is translating to U.S. companies’ profit and sales forecasts. This month, 45 and 43 percent of our respondents say they’re projecting profits and revenues to increase over the coming year, respectively, compared to 37 and 40 percent last month. That represents an increase of 111 percent and 72 percent, respectively, since the bottom of the crisis in early April.
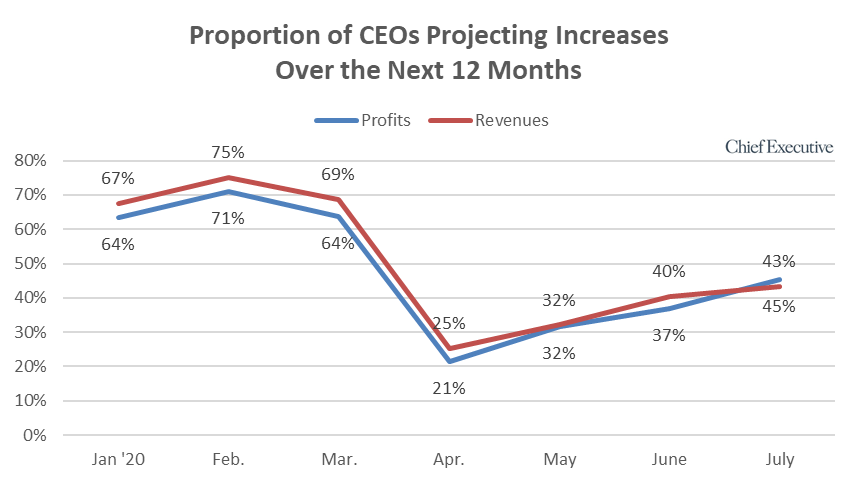
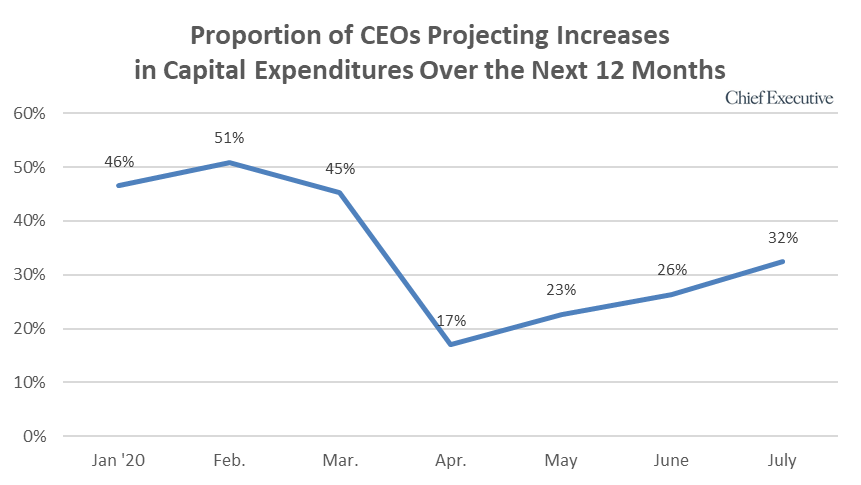
"We see a similar trend when looking at the proportion of CEOs who anticipate increases in capital expenditures, up 23 percent month-over-month and 91 percent since the trough in April.
"The only measure that remains somewhat flat in July is the outlook for hiring. A quarter of CEOs said they’re planning to add to their workforce in the months ahead—unchanged from June—which is somewhat higher than when we polled CEOs in April, when only 18 percent of CEOs said they’d be hiring more staff.
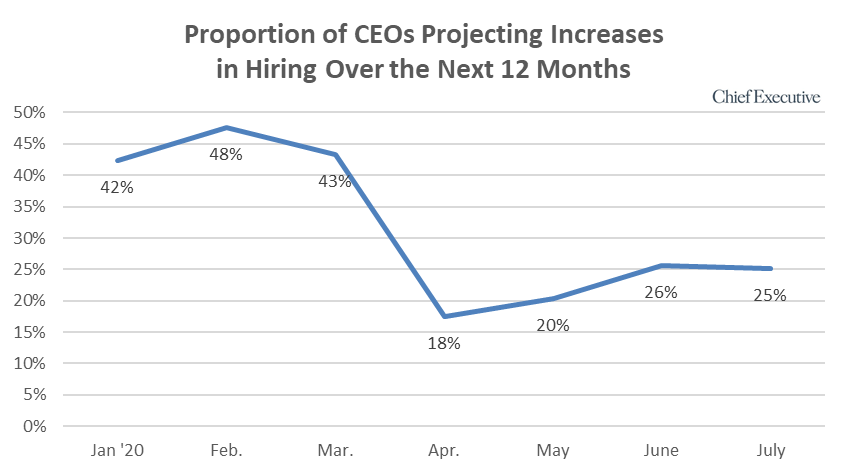
"Some CEOs say they are finding it difficult to hire the right talent in their regions, despite the high unemployment rate, while others say they are temporarily freezing their recruiting to match their sales expectations.
“'Even though unemployment remains very high, it is nearly impossible to hire adequate staff to run our operations in MI and MS,' said John Gessert, president of American Plastic Toys, a mid-sized manufacturer in the Midwest.
"For months now, we have been monitoring the tapering of negative forecasts across all four indicators (revenue, profit, headcount and capex), with fewer and fewer CEOs reporting anticipating decreases over the coming year. The charts above highlight the continuation of this trend into Q3.
Sector View
"Looking at the data by industry, the outlook among CEOs in 8 of the 14 sectors covered by the survey are positive month over month, with the government/non-profit sector leading the way with a gain of 30 percent. This is quite a comeback for that sector, after losing 14 percent last month. While CEOs in that group say they remain concerned about the long-term impact of the crisis, they have optimism about a vaccine or treatment for the coronavirus.
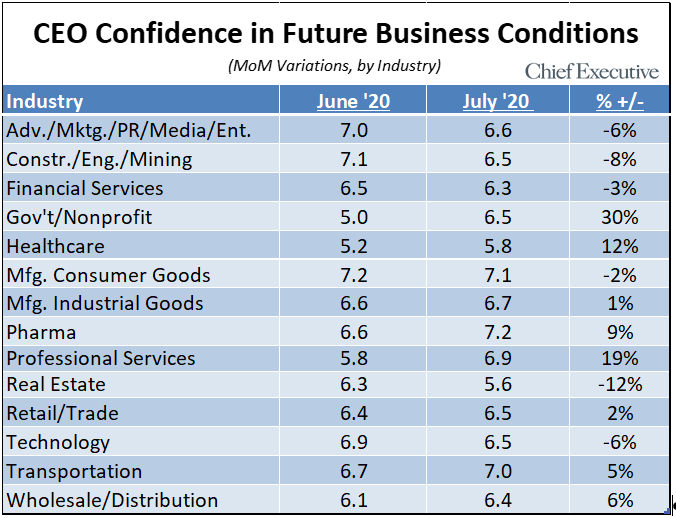
"Healthcare also had a substantial reversal this month, up 12 percent after losing 29 percent last month. Confidence in that sector has been highly volatile since the beginning of the pandemic, fluctuating between near 30-percent drops and near 20-percent climbs. Healthcare CEOs who participated in the survey say that while they are concerned about the crisis and its effect on healthcare programs, particularly Medicaid, the rate of recovery in patients who contract the virus is fueling optimism that the situation may not be as dire as initially communicated.

"Year over year, the data paints a similarly mixed story, with some industries up double digits and others down by the same margins—all highlighting the extreme volatility this crisis is having on business.
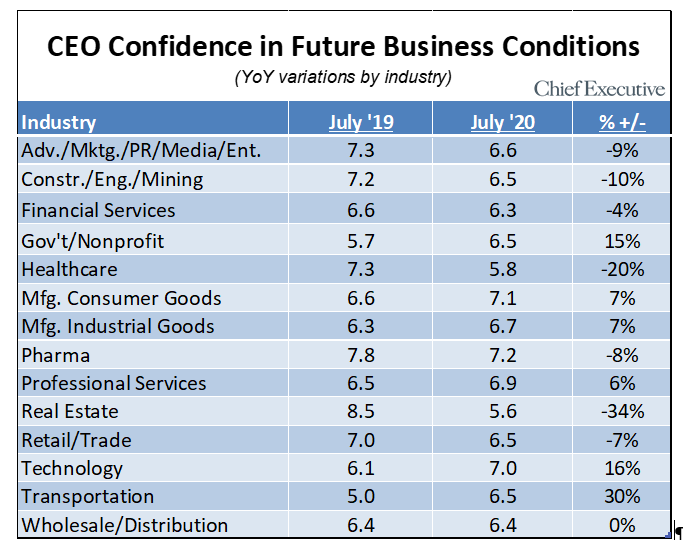
"When looking at CEO confidence by company size (annual revenues), small company CEOs had the largest increase, up 7 percent month over month. Many of the CEOs in that peer group say they are gradually getting operations back online with losses that were less than initially projected.
"As has been the case for the past few months, large companies remain the least optimistic in future business conditions. CEOs in that group point to the upcoming election as one of the main factors in that cautious stance, with concerns over tax increases and new regulations.

About the CEO Confidence Index
"The CEO Confidence Index is America’s largest monthly survey of chief executives. Each month, Chief Executive surveys CEOs across America, at organizations of all types and sizes, to compile our CEO Confidence Index data. The Index tracks confidence in current and future business environments, based on CEOs’ observations of various economic and business components."
Types of CNC machines
Curious about the different types of machines that are used in CNC manufacturing? Consider this.
According to John Saunders with London Loves Business:
"CNC machine manufacturing as the name suggests is a computer-controlled manufacturing process. Over time, they have become quite popular with manufacturers. It offers numerous advantages to manufacturers with the most important one being automation.
"CNC machines help factories get around major problems caused by labor shortages. They are automatic and carry out a large load of work, that may need hundreds of workers to implement.
"They also help lower manufacturing costs, through speedy and accurate production.
"Here are some types of CNC machines that companies can invest in to improve their manufacturing process, and product quality.
CNC milling machines
"This is one of the loved and most common CNC machines. The milling machine uses in-built rotary cutters for drilling and cutting. Once the materials are placed in it, the computer then guides the rotary cutters on whether to cut or drill the materials it is working on. A CNC machine is highly accurate and precise.
"Usually the milling machine is a three-axis machine. However, it is also available in 4 to 6 axes for more angles to cut and deliver high quality products.
CNC routers
"This is another common type of milling machine. CNC routers do not require any human interaction. They are completely computer controlled. Also, a three-axis machine, CNC routers majorly work on wood, metal sheets and plastic materials.
"Further CNC machines are meant to work on large products.
CNC plasma machine
"Another common type of CNC machine is the plasma cutting machine. This is a cutting tool that uses a laser torch to cur through wood and metal sheets.
"The CNC plasma cutting machine is a two-axis machine. In addition, it does not require as much power as the milling machine to perform its duties. It is therefore suitable for small manufacturers who deal with wood and metal sheets.
CNC laser machine
"Unlike the CNC plasma machine, the CNC laser machine cuts with a laser. It is therefore more precise and accurate than its the plasma torch machine. Depending on the material it is working on, the strength of the laser needs to be varied. This machine is suitable for manipulating wood, metal sheets and plastic sheets.
"Like the plasma machine, the laser machine is highly flexible and easily creates as many shapes as can be required.
CNC lathe machines
"If you want to create a spherical or cone shape on metal sheets and products, this is the machine to use. It usually has a rotating part and spindle that shaves of the product slowly by slowly to create the perfect circular shape.
CNC pick and place machines
"CNC pick and place machines are the machines used to assemble sensitive components of electrical appliances such as TVs and mobile devices and laptops. They are highly accurate and for that reason are used for such critical tasks as electrical devices assembly. They are highly capable thanks to their several pairs of arms that can suction pieces and fix them exactly where they need to be.
CNC grinders
"This is a CNC machine that grinds metal sheets with a rotary wheel. As a computer-controlled machine, it does not require extreme precision and thus it may be the easiest to use among all the types of CNC machines.
CNC metrology machines
"CNC metrology machines are machines that are used to inspect other machines. They check for accuracy in dimensions. As CNC machines, they carry out their tasks via a 3 -D software. They help to check on the tolerance of machines to ensure that products are made in the correct dimensions.
Conclusion
"There exist numerous types of CNC machines. Different companies can acquire different types of machines depending on the type of work that they carry out. CNC machines automate factories and make work easier to perform and carry out. With little human intervention, CNC machines are highly automatic and rarely if ever produce work that does not meet expectations."
Machine Market 2020 Booming Worldwide
The current market for CNC machines is seeing a boom worldwide.
According to Cole Market Research:
"Global CNC Machine Market Research Report’, the report is complete with an elaborate research undertaken by prominent analysts and a detailed analysis of the global industry place. The study is inclusive of a well-elaborated, extensive scrutiny of this industry alongside major parameters that may most likely have an influence on the market commercialization matrix. A SWOT analysis can be quite handy when it comes to determining the drivers and restraints of the CNC Machine market. The CNC Machine report aims to underline all the key aspects of the CNC Machine market to keep you updated about the recent happenings of the market, for instance, key players and brand’s acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures, recent developments, products launches, and the competitive research. The competition is expected to intensify in the upcoming years and augment the need for proper strategizing for business players. The CNC Machine report further explains the market definition, classifications, applications, engagements, and global reach is for the CNC Machine industry while giving a CAGR forecast for the period of 2020 and 2027. Few of the major competitors currently working in the global CNC Machine market are AMADA MACHINE TOOLS CO., LTD.; Amera-Seiki Corporation; DMG MORI CO., LTD.; SCM Group; General Technology Group Dalian Machine Tool Corporation; DATRON; FANUC CORPORATION; Haas Automation, Inc – CNC Machine Tools; Hurco Companies, Inc.;
"Global CNC machine market is expected to rise to an estimated value of USD 113.54 billion by 2026, registering a substantial CAGR in the forecast period of 2019-2026. This rise in market value can be attributed to the growing demand for reducing the operational costs associated with the operational costs of the end-use manufacturing industries.
"Global CNC Machine Market Dynamics:
"Market Drivers:
"Rapid demand for effective machineries from industries that provide high levels of productivity with lower amount of down time
Surge in the availability of IoT technology, as well as machine learning resulting in the various beneficial features associated with the machines is expected to augment growth of the market
Growing demand for equipments and machineries that can handle mass-production at an effective and efficient scale is expected to drive the growth of the market
Market Restraints:
"Large costs associated with the purchasing of these machines as well as the costs associated with their maintenance; this factor is expected to restricts the growth of the market
Investments in the establishment of these machineries result in greater unemployment rate due to the lack of engineers and individuals required to operate these machineries also restricts the growth of the market
"Important Features of the Global CNC Machine Market Report:
"1) What all companies are currently profiled in the report?
"List of players that are currently profiled in the report- Okuma Corporation; Yamazaki Mazak Corporation; Shenyang Machine Tools Co.,Ltd.; Ellison Technologies, Inc.; The Lincoln Electric Company; Fagor Automation; GSK CNC EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD.; HEIDENHAIN; Smiths Machine; MAG IAS GmbH; JTEKT Corporation; GF Machining Solutions Management SA; Hyundai WIA among others.
"2) What all regional segmentation covered? Can specific country of interest be added?
"Currently, research report gives special attention and focus on following regions:
"North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific etc.
"3) Can inclusion of additional Segmentation / Market breakdown is possible?
Global CNC Machine Market Segmentation:
By Type
"Lathe Machines
"Milling Machines
"Laser Machines
"Grinding Machines
"Welding Machines
"Winding Machines
"Others
By Application
"Machinery Manufacturing
"Automobiles
"Electronics
"Healthcare
"Aerospace & Defense
By End-Use
"Automotive
"Aerospace & Defense
"Construction Equipment
"Power & Energy
"Industrial
"Others
"Region wise analysis of the top producers and consumers, focus on product capacity, production, value, consumption, market share and growth opportunity in below mentioned key regions:
"North America – U.S., Canada, Mexico
"Europe : U.K, France, Italy, Germany, Russia, Spain, etc.
"Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, India, Southeast Asia etc.
"South America – Brazil, Argentina, etc.
"Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, African countries etc.
Key Highlights from CNC Machine Market Study.
"Revenue and Sales Estimation — Historical Revenue and sales volume is presented and further data is triangulated with top-down and bottom-up approaches to forecast complete market size and to estimate forecast numbers for key regions covered in the report along with classified and well recognized Types and end-use industry. Additionally macroeconomic factor and regulatory policies are ascertained in CNC Machine industry evolution and predictive analysis.
"Manufacturing Analysis —the report is currently analyzed concerning various product type and application. The CNC Machine market provides a chapter highlighting manufacturing process analysis validated via primary information collected through Industry experts and Key officials of profiled companies.
"Competition — Leading players have been studied depending on their company profile, product portfolio, capacity, product/service price, sales, and cost/profit.
"Demand & Supply and Effectiveness — CNC Machine report additionally provides distribution, Production, Consumption & EXIM** (Export & Import). ** If applicable
Key Highlights of Report
"Overview of key market forces propelling and restraining market growth
"Offers a clear understanding of the competitive landscape and key product segments
"An analysis of strategies of major competitors
"Detailed analyses of industry trends
"A well-defined technological growth map with an impact-analysis
"Provides profiles of major competitors of the market.
"Details of their operations, product and services.
"Recent developments and key financial metrics."
Stainless Steel Forgings Market
The stainless steel forgings market is set to see growth in the next five years, according to some. Consider this report.
According to 3rd Market Report and Analytics:
"Forging is a manufacturing procedure which involves the shaping of material with a hammer using compressive force. Stainless steel is a widely use material among manufacturers to develop industrial parts. Manufacturers select stainless steel material based on its corrosion resistance, strength, heat resistance as well as other mechanical properties. The main advantage of stainless steels material includes resistance to corrosion by atmospheric conditions, moisture, and other violent environments at low or high temperature. Fabrication is a significant factor required even in the early stage of product design along with forging which is one of the manufacturing method adopted by designers. Forged parts are widely used in machines and mechanisms.
"Additionally, the stainless steel forgings technique provide an advanced, and continuous grain flow that follows the contour of part unlike different techniques such as machining or casting. Therefore, through gain flow and refinement, forging allows the strength where it required most coupled with improving the mechanical properties of stainless steel the forgings will enhance the overall product part quality.
Stainless Steel Forgings Market: Drivers and Restraints
"Stainless steel forgings market is witnessing maximum growth owing to expanding demand for lightweight forged products, developing manufacturing activities globally, growing demand for commissioned products, and enhancing the use of stainless steel in various end use application. Moreover, expansion in the construction industry, increasing regime expenditure, and advanced features such as excellent inherent forgeability, higher ductility, cryogenic toughness, lower maintenance, and heat resistance are some of the factors that can boost the demand for stainless steel forgings over the forecast period. However, alternative materials used in the manufacturing of forgings such as plastic, and aluminum coupled with volatile raw material costs such as chromium and nickel may hamper the growth of the stainless steel forgings market during the forecast period.
Stainless Steel Forgings Market: Segmentation
"The stainless steel forgings market has been classified on the basis of product type, process type, shape and application.
Based on product type, the stainless steel forgings market is segmented into the following:
Castings
Hot/Cold Forged Parts
Sintered Parts
Based on process type, the stainless steel forgings market is segmented into the following:
Open Die Forging
Closed Die or Impression Die Forging
Impression Die Forging
Extrusion
Others
Based on shape, the stainless steel forgings market is segmented into the following:
Forged Rings
Discs
Blocks
Flat Bars
Round Bars
Others
Based on application, the stainless steel forgings market is segmented into the following:
Automotive
Aerospace
Industrial
Building & Construction
Consumer Goods
Aviation
Others
Stainless Steel Forgings Market: Overview
"Stainless steel forgings market revenue is expected to grow at a rapid growth rate, over the forecast period. The market is anticipated to perform well in the near future owing to its favorable properties such as high strength, reliability, wear & tear resistance, product versatility, economy viability, and high corrosion resistance. Additionally, it is also used for the manufacturing of various aviation components such as hinges, bulkheads, engine mounts, beams, wing roots, landing gear cylinders, and arresting hooks are some of the factors that can propel the market revenue growth of stainless steel forgings in the near future. Based on product type, castings segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period attributed to the manufacturing of complex designs that would be otherwise difficult to form by other processing methods.
Stainless Steel Forgings Market: Region-wise Outlook
"Depending on the geographic region, stainless steel forgings market is divided into seven key regions: North America, Eastern Europe, Latin America, Western Europe, Japan, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa. North America dominates the stainless steel forgings market followed by Europe, and Japan is owing to rapidly increase in the aerospace manufacturing industry which is further expanding the demand for defense aircraft, high consumption of forgings, and the presence of key manufacturers in these regions. The market in Asia Pacific and Japan is expected to grow at significant CAGR owing to expanding automotive industry in developing countries such as China, and India along with increasing foreign investment, and a rise in construction projects are some of the factors that are projected to propel the growth of stainless steel forgings market throughout the forecast period."
Next-generation grinding software cuts turnaround time in half
For those looking to reduce turnaround time, new grinding software can potentially cut that time in half.
According to Cutting Tool Engineering:
"As a specialty toolmaker, Dew Tool Grinding Services Inc. always has relied heavily on the software of tool grinding machines. However, as those machines aged, the Oak Creek, Wis., shop realized that it needed the added functionality and capabilities of newer versions of tool grinding machine software to not only meet customer deliveries for more complex tools, but also to boost its overall competitiveness.
"According to Operations Engineering Manager and part owner of Dew Tools Tim Kirst, the shop makes specialty cutting tools for valve and medical device manufacturers and job shops producing parts for companies such as John Deere and Caterpillar. The shop makes three types of cutting tools that include basic high-speed steel tools, carbide tools and carbide-tipped tools. In fact, Dew Tool is one of the few shops in its area making carbide-tipped tooling.
"The shop is a long-time user and fan of WALTER tool grinding machines from Walter Maschinenbau GmbH, a member of the UNITED GRINDING Group, and purchased its first one in 1999 and another in 2006.
“'WALTER machines are the best fit for what we do,' explained Kirst. 'We’re not a big re-grind house. The business lies in more technical step tooling, and the software the WALTER machines come equipped with, even in 1999, is far better than that offered by other manufacturers’ machines. But once we learned of the new HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO software and all it could do, we knew it would provide us with the boost in efficiency, cost savings and speed we were looking for to be more competitive in today’s manufacturing environment.'
"The HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO, CAD/CAM software for design, programming, simulation and production came with Dew Tool’s new WALTER HELITRONIC BASIC 5-axis machine. The extremely rigid, gantry design machine sharpens and grinds a wide spectrum of precision tools and offers complete machining in single clamping cycles. Its field of applications covers all rotationally symmetrical tools for machining metal as well as special tools and parts with complex geometries. And, according to Kirst, the machine and its software proved to be a game changer.
"The software combines ease of programming with the greatest possible flexibility. With minimum complexity, Dew Tool operators can easily program machining steps and movement sequences for both rotationally symmetrical standard tools and specialty tools. In operation, the tool depicted on the machine’s CNC display corresponds exactly with the tool being machined – a feature based off the tried and true method of “what you see is what you grind.” This means that, as early as the design phase, Dew Tool can review the finished part via true-to-life 3D simulation. If necessary, the shop can make programming corrections before the machine’s grinding wheel ever touches the part, saving time and money. It’s a feature Kirst particularly finds most beneficial.
“'The leap from Walter Window Mode, which was the software on the older machines, to HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO has just been absolutely phenomenal,' Kirst said. 'Turnaround time means everything for our shop, and it was the one area that had, over the years, grown to be a challenge for us. With our new WALTER and its HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO software, we’ve been able to speed up delivery from three or four weeks down to only two, allowing us to better compete. Our customers always knew they were getting a good custom tool from us, and now they’re getting it faster, which is improving their experience. That’s where I see the difference.'
"Although Kirst was a little apprehensive about a new software program, it didn’t take very long for him to learn and discover all of its improvements.
“'Being able to grind the tool virtually on screen, before we even put a wheel in motion, has already saved me countless dollars in wheels as well as in raw material,' said Kirst. 'We also saw immediate improvements in the quality of our tools because we know exactly where the wheel is going to go and what it's going to grind before we start. If I need to make three parts for a customer, I get three perfect parts. I no longer have to make four or five to get those perfect three.'
"Kirst also likes the ability to program and verify programs offline from a PC with HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO, which is particularly important because of the complex parts the shop produces. This capability eliminates the need to stop after each operation, giving the shop more confidence in the accuracy of the tools being produced.
“'With HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO, we’re able to program offline and transfer the program to the machine from a memory stick,' he added. 'That saves a lot of time, and it’s usually correct with very little adjustment needed. Before HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO, we had to be very cautious about how the machine was going to be set up and come in for the next grind. The accuracy with HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO was a huge improvement in productivity for us.'
"Another feature of the software helping Kirst’s shop be more productive is HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO’s Assistant, called Wizard, which provides common programming parameters that can be entered for standard tool families and Knowledge Base, which provides recommended speeds and feeds for different operations.
“'These recommendations have also made a tremendous improvement because we're running a lot faster. Because of the way the new software is grinding drills, for example, and applying the recommended speeds and feeds, we've taken drill pointing from 15 minutes on our other machines to maybe four to five minutes on the new one,' he said.
"Additionally, the software has all but removed the shop’s need for manual operations, saving money, improving quality and reducing time for other processes. The shop has also been able to adjust speeds and feeds – based on parameters from HELITRONIC TOOL STUDIO – to further boost the output of its older WALTER machines.
"The new machine’s efficiency and productivity also frees up some of Kirst’s time, so he spends less of it in actual shop operations and more of it building his business. He’s currently in discussions to secure more prototyping work from another local company, and, because the new WALTER has also added capacity to his operations, he is now working on expanding his client base within the Midwest and across the nation.
“'Every time someone has to handle a part, it costs money,' explained Kirst. 'The new WALTER has allowed us to be more competitive with our pricing because, for some parts, we’re looking at 15-20 minutes compared to an hour and 15 minutes, so the machine and its technology has made an impact on our bottom line by being faster, and, at the same time, allowing me to optimize my workforce.'
"Dew Tool opened for business in 1983 as a one-man shop and Kirst became part owner in 2000. He’s spent his entire career in the machine shop business – he started right out of high school in an aerospace machine shop – and has seen a lot. One thing he’s certain about is the importance of investing in the latest grinding technologies, and that includes software.
“'It’s just good business to keep up with the advances in modern manufacturing, from both a business success and customer experience perspective. UNITED GRINDING has been a long time trusted partner in helping us make that happen,' he said."
Understanding CNC Milling
From the surface, CNC milling can seem complicated. Consider this breakdown.
According to Thomas Net:
"CNC milling, or computer numerical control milling, is a machining process which employs computerized controls and rotating multi-point cutting tools to progressively remove material from the workpiece and produce a custom-designed part or product. This process is suitable for machining a wide range of materials, such as metal, plastic, glass, and wood, and producing a variety of custom-designed parts and products.
"Several capabilities are offered under the umbrella of precision CNC machining services, including mechanical, chemical, electrical, and thermal processes. CNC milling is a mechanical machining process along with drilling, turning, and a variety of other machining processes, meaning that material is removed from the workpiece via mechanical means, such as the actions of the milling machine’s cutting tools.
"This article focuses on the CNC milling process, outlining the basics of the process, and the components and tooling of the CNC milling machine. Additionally, this article explores the various milling operations and provides alternatives to the CNC milling process.
Overview of CNC Milling Process
"Like most conventional mechanical CNC machining processes, the CNC milling process utilizes computerized controls to operate and manipulate machine tools which cut and shape stock material. In addition, the process follows the same basic production stages which all CNC machining processes do, including:
Designing a CAD model
Converting the CAD model into a CNC program
Setting up the CNC milling machine
Executing the milling operation
"The CNC milling process begins with the creation of a 2D or 3D CAD part design. Then the completed design is exported to a CNC-compatible file format and converted by CAM software into a CNC machine program which dictates the actions of the machine and the movements of the tooling across the workpiece. Before the operator runs the CNC program, they prepare the CNC milling machine by affixing the workpiece to the machine’s work surface (i.e., worktable) or workholding device (e.g., vise), and attaching the milling tools to the machine spindle. The CNC milling process employs horizontal or vertical CNC-enabled milling machines—depending on the specifications and requirements of the milling application—and rotating multi-point (i.e., multi-toothed) cutting tools, such as mills and drills. When the machine is ready, the operator launches the program via the machine interface prompting the machine to execute the milling operation.
"Once the CNC milling process is initiated, the machine begins rotating the cutting tool at speeds reaching up to thousands of RPM. Depending on the type of milling machine employed and the requirements of the milling application, as the tool cuts into the workpiece, the machine will perform one of the following actions to produce the necessary cuts on the workpiece:
Slowly feed the workpiece into the stationary, rotating tool
Move the tool across the stationary workpiece
Move both the tool and workpiece in relation to each other
"As opposed to manual milling processes, in CNC milling, typically the machine feeds moveable workpieces with the rotation of the cutting tool rather than against it. Milling operations which abide by this convention are known as climb milling processes, while contrary operations are known as conventional milling processes.
"Generally, milling is best suited as a secondary or finishing process for an already machined workpiece, providing definition to or producing the part’s features, such as holes, slots, and threads. However, the process is also used to shape a stock piece of material from start to finish. In both cases, the milling process gradually removes material to form the desired shape and form of the part. First, the tool cuts small pieces—i.e., chips—off the workpiece to form the approximate shape and form. Then, the workpiece undergoes the milling process at much higher accuracy and with greater precision to finish the part with its exact features and specifications. Typically, a completed part requires several machining passes to achieve the desired precision and tolerances. For more geometrically complex parts, multiple machine setups may be required to complete the fabrication process.
"Once the milling operation is completed, and the part is produced to the custom-designed specifications, the milled part passes to the finishing and post-processing stages of production.
CNC Milling Operations
"CNC milling is a machining process suitable for producing high accuracy, high tolerance parts in prototype, one-off, and small to medium production runs. While parts are typically produced with tolerances ranging between +/- 0.001 in. to +/- 0.005 in., some milling machines can achieve tolerances of up to and greater than +/- 0.0005 in. The versatility of the milling process allows it to be used in a wide range of industries and for a variety of part features and designs, including slots, chamfers, threads, and pockets. The most common CNC milling operations include:
Face milling
Plain milling
Angular milling
Form milling
Face Milling
"Face milling refers to milling operations in which the cutting tool’s axis of rotation is perpendicular to the surface of the workpiece. The process employs face milling cutters which have teeth both on the periphery and tool face, with the peripheral teeth primarily being used for cutting and the face teeth being used for finishing applications. Generally, face milling is used to create flat surfaces and contours on the finished piece and is capable of producing higher quality finishes than other milling processes. Both vertical and horizontal milling machines support this process.
"Types of face milling include end milling and side milling, which use end milling cutters and side milling cutters, respectively.
Plain Milling
"Plain milling, also known as surface or slab milling, refers to milling operations in which the cutting tool’s axis of rotation is parallel to the surface of the workpiece. The process employs plain milling cutters which have teeth on the periphery that perform the cutting operation. Depending on the specifications of the milling application, such as the depth of the cut and the size of the workpiece, both narrow and wide cutters are used. Narrow cutters allow for deeper cuts, while wider cutters are used for cutting larger surface areas. If a plain milling application requires the removal of a large amount of material from the workpiece, the operator first employs a coarse-toothed cutter, slow cutting speeds, and fast feed rates to produce the custom-designed part’s approximate geometry. Then, the operator introduces a finer toothed cutter, faster cutting speeds, and slower feed rates to produce the details of the finished part.
Angular Milling
"Angular milling, also known as angle milling, refers to milling operations in which the cutting tool’s axis of rotation is at an angle relative to the surface of the workpiece. The process employs single-angle milling cutters—angled based on the particular design being machined—to produce angular features, such as chamfers, serrations, and grooves. One common application of angular milling is the production of dovetails, which employs 45°, 50°, 55°, or 60° dovetail cutters based on the design of the dovetail.
Form Milling
"Form milling refers to milling operations involving irregular surfaces, contours, and outlines, such as parts with curved and flat surfaces, or completely curved surfaces. The process employs formed milling cutters or fly cutters specialized for the particular application, such as convex, concave, and corner rounding cutters. Some of the common applications of form milling include producing hemispherical and semi-circular cavities, beads, and contours, as well as intricate designs and complex parts with a single machine setup.
Other Milling Machine Operations
"Besides the aforementioned operations, milling machines can be used to accomplish other specialized milling and machining operations. Examples of the other types of milling machine operations available include:
"Straddle milling: Straddle milling refers to milling operations in which the machine tool machines two or more parallel workpiece surfaces with a single cut. This process employs two cutters on the same machine arbor, arranged such that the cutters are at either side of the workpiece and can mill both sides at the same time.
"Gang milling: What is gang milling? Gang milling refers to milling operations which employ two or more cutters—typically of varying size, shape, or width—on the same machine arbor. Each cutter can perform the same cutting operation, or a different one, simultaneously, which produces more intricate designs and complex parts in shorter production times.
"Profile milling: Profile milling refers to milling operations in which the machine tool creates a cut path along a vertical or angled surface on the workpiece. This process employs profile milling equipment and cutting tools which can be either parallel or perpendicular to the workpiece’s surface.
"Gear cutting: Gear cutting is a milling operation which employs involute gear cutters to produce gear teeth. These cutters, a type of formed milling cutters, are available in various shapes and pitch sizes depending on the number of teeth necessary for the particular gear design. A specialized lathe cutter bit can also be employed by this process to produce gear teeth.
"Other machining processes: Since milling machines support the use of other machine tools besides milling tools, they can be used for machining processes other than milling, such as drilling, boring, reaming, and tapping.
CNC Milling Equipment and Components
"The CNC milling process employs a variety of software applications, machine tools, and milling machinery depending on the milling operation being performed.
CNC Support Software
"Like most CNC machining processes, the CNC milling process uses CAD software to produce the initial part design and CAM software to generate the CNC program which provides the machining instructions to produce the part. The CNC program is then loaded to the CNC machine of choice to initiate and execute the milling process.
CNC Milling Machine Components
"Despite the wide range of milling machines available, most machines largely share the same basic components. These shared machine parts include the:
Machine interface
Column
Knee
Saddle
Worktable
Spindle
Arbor
Ram
Machine tool
"Machine interface: The machine interface refers to the machine component the operator uses to the load, initiate, and execute the CNC machine program.
"Column: The column refers to the machine component which provides support and structure to all other machine components. This component includes an affixed base and can include additional internal components which aid the milling process, such as oil and coolant reservoirs.
"Knee: The knee refers to the adjustable machine component which is affixed to the column and provides support to the saddle and worktable. This component is adjustable along the Z-axis (i.e., able to be raised or lowered) depending on the specifications of the milling operation.
"Saddle: The saddle refers to the machine component located on top of the knee, supporting the worktable. This component is capable of moving parallel to the axis of the spindle, which allows the worktable, and by proxy the workpiece, to be horizontally adjusted.
"Worktable: The worktable refers to the machine component located on top of the saddle, which the workpiece or workholding device (e.g., chuck or vise) is fastened. Depending on the type of machine employed, this component is adjustable in the horizontal, vertical, both, or neither direction.
"Spindle: The spindle refers to the machine component supported by the column which holds and runs the machine tool (or arbor) employed. Within the column, an electric motor drives the rotation of the spindle.
"Arbor: The arbor refers to the shaft component inserted into the spindle in horizontal milling machines in which multiple machine tools can be mounted. These components are available in various lengths and diameters depending on the specifications of the milling application. The types of arbors available include standard milling machine, screw, slitting saw milling cutter, end milling cutter, and shell end milling cutter arbors.
"Ram: The ram refers to the machine component, typically in vertical milling machines, located on top of and affixed to the column which supports the spindle. This component is adjustable to accommodate different positions during the milling operation.
"Machine tool: The machine tool represents the machine component held by the spindle which performs the material removal operation. The milling process can employ a wide range of milling machine tools (typically multi-point cutters) depending on the specifications of the milling application—e.g., the material being milled, quality of the surface finish required, machine orientation, etc. Machine tools can vary based on the number, arrangement, and spacing of their teeth, as well as their material, length, diameter, and geometry. Some of the types of horizontal milling machine tools employed include plane, form relieved, staggered tooth, and double angle mills, while vertical milling machine tools employed include flat and ball end, chamfer, face, and twist drill mills. Millings machines can also use drilling, boring, reaming, and tapping tools to perform other machining operations.
Milling Machine Considerations
"In general, milling machines are categorized into horizontal and vertical machine configurations, as well as differentiated based on the number of axes of motion.
"In vertical milling machines, the machine spindle is vertically oriented, while in horizontal milling machines the spindle is horizontally oriented. Horizontal machines also employ arbors for additional support and stability during the milling process, and have support capabilities for multiple cutting tools, such as in gang milling and straddle milling. Controls for both vertical and horizontal milling machine are dependent on the type of machine employed. For example, some machines can raise and lower the spindle and laterally move the worktable, while other machines have stationary spindles and worktables which move both horizontally, vertically, and rotationally. When deciding between vertical and horizontal milling machines, manufacturers and job shops must consider the requirements of the milling application, such as the number of surfaces requiring milling and the size and shape of the part. For example, heavier workpieces are better suited for horizontal milling operations, while die sinking applications are better suited for vertical milling operations. Ancillary equipment that modifies vertical or horizontal machines to support the opposing process is also available.
"Most CNC milling machines are available with 3 to 5 axes— typically providing performance along the XYZ axes and, if applicable, around rotational axes. The X-axis and Y-axis designate horizontal movement (side-to-side and forward-and-back, respectively, on a flat plane), while the Z-axis represents vertical movement (up-and-down) and the W-axis represents diagonal movement across a vertical plane. In basic CNC milling machines, horizontal movement is possible in two axes (XY), while newer models allow for the additional axes of motion, such as 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC machines...
"Depending on the type of milling machine employed, the machine tool, the machine worktable, or both of the components can be dynamic. Typically, dynamic worktables move along the XY-axes, but they are also capable of moving up and down to adjust the depth of cut and swiveling along the vertical or horizontal axis for an increased range of cutting. For milling applications requiring dynamic tooling, in addition to its inherent rotary motion, the machine tool moves perpendicularly along multiple axes, allowing the tool’s circumference, rather than just its tip, to cut into the workpiece. CNC milling machines with greater degrees of freedom allow for greater versatility and complexity in the milled parts produced.
Types of Milling Machines
"There are several different types of milling machines available which are suitable for a variety of machining applications. Beyond classification based solely on either machine configuration or the number of axes of motion, milling machines are further classified based on the combination of their specific characteristics. Some of the most common types of milling machines include:
Knee-type
Ram-type
Bed-type (or manufacturing-type)
Planer-type
"Knee-type: Knee-type milling machines employ a fixed spindle and vertically adjustable worktable which rests on the saddle supported by the knee. The knee can be lowered and raised on the column depending on the position of the machine tool. Some examples of knee-type milling machines include floor-mounted and bench-type plain horizontal milling machines.
"Ram-type: Ram-type milling machines employ a spindle affixed to a movable housing (i.e., ram) on the column, which allows the machine tool to move along the XY axes. Two of the most common ram-type milling machines include floor-mounted universal horizontal and swivel cutter head milling machines.
"Bed-type: Bed-type milling machines employ worktables affixed directly to the machine bed, which prevents the workpiece from moving along both the Y-axis and Z-axis. The workpiece is positioned beneath the cutting tool, which, depending on the machine, is capable of moving along the XYZ axes. Some of the bed-type milling machines available include simplex, duplex, and triplex milling machines. While simplex machines employ one spindle which moves along either the X-axis or Y-axis, duplex machines employ two spindles, and triplex machines employ three spindles (two horizontal and one vertical) for machining along the XY and XYZ axes, respectively.
"Planer-type: Planer-type milling machines are similar to bed-type milling machines in that they have worktables fixed along the Y-axis and Z-axis and spindles capable of moving along the XYZ axes. However, planer-type machines can support multiple machine tools (typically up to four) simultaneously, which reduces the lead time for complex parts.
"Some of the specialized types of milling machines available include rotary table, drum, and planetary milling machines. Rotary table milling machines have circular worktables which rotate around the vertical axis and employ machine tools positioned at varying heights for roughing and finishing operations. Drum milling machines are similar to rotary table machines, except the worktable is referred to as a “drum” and it rotates around the horizontal axis. In planetary machines, the worktable is stationary, and the workpiece is cylindrical. The rotating machine tool moves across the surface of the workpiece cutting internal and external features, such as threads.
Material Considerations
"The CNC milling process is best suited as a secondary machining process to provide finishing features to a custom-designed part, but can also be used to produce custom designs and specialty parts from start to finish. CNC milling technology allows the process to machine parts of a wide range of materials, including:
Metals (including alloy, exotic, heavy duty, etc.)
Plastics (include thermosets and thermoplastics)
Elastomers
Ceramics
Composites
Glass
"As with all machining processes, when selecting a material for a milling application, several factors must be considered, such as the properties of the material (i.e., hardness, tensile and shear strength, and chemical and temperature resistance) and the cost-effectiveness of machining the material. These criteria dictate whether the material is suitable for the milling process and the budgetary constraints of the milling application, respectively. The chosen material determines the type(s) of the machine tool(s) employed and its/their design(s), and the optimal machine settings, including cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut.
Alternatives
"CNC milling is a mechanical machining process suitable for machining a wide range of materials and producing a variety of custom-designed parts. While the process may demonstrate advantages over other machining processes, it may not be appropriate for every manufacturing application, and other processes may prove more suitable and cost-effective.
"Some of the other more conventional mechanical machining processes available include drilling and turning. Drilling, like milling, typically employs multi-point tools (i.e., drill bits), while turning employs single-point tools. However, while in turning the workpiece can be moved and rotated similar to that of some milling applications, in drilling the workpiece is stationary throughout the drilling operation.
"Some of the non-conventional mechanical machining processes (i.e., do not employ machine tools but still employ mechanical material removal processes) include ultrasonic machining, waterjet cutting, and abrasive jet machining. Non-conventional, non-mechanical machining processes—i.e., chemical, electrical, and thermal machining processes—provide additional alternative methods of removing material from a workpiece which do not employ machine tools or mechanical material removal processes, and include chemical milling, electrochemical deburring, laser cutting, and plasma arc cutting. These non-conventional machining methods support the production of more complex, demanding, and specialized parts not typically possible through conventional machining processes.
Summary
"Outlined above are the basics of the CNC milling process, various CNC milling operations and their required equipment, and some of the considerations that may be taken into account by manufacturers and machine shops when deciding whether CNC milling is the most optimal solution for their particular machining application."
Considerations When Working With Prototyping Outsourcers
Working with outsourcers can be a challenge, but with prototyping there are more things to consider.
According to Robotics Business Review:
"In order to survive and stay relevant, companies in today’s ultra-competitive markets must instantly respond to market demand and find ways to speed their time. As prototyping is an important part of the whole product lifecycle, manufacturing and design engineers need custom prototypes for testing, fit check, and other technical pre-measures.
"Yet, what is the most efficient way to make and source prototypes? While bigger companies most often have the resources to produce their prototypes in-house, startups and smaller companies may not have the necessary equipment and expertise required to manufacture a single prototype or small runs of parts. There are many specialized companies in prototyping services and short-run manufacturing, and they represent a stellar option for small and medium businesses that need this type of service.
"In manufacturing prototypes, it’s important to consider the materials and process technology to use for every project. Some prototypes must be made of the same material as the production part, while other prototypes, such as prototypes used for concept or presentation, can be made of a lower-cost or faster-to-build material. In this article, first, we’re going to note the importance of prototyping as a pre-manufacturing process, and later we will point out the most important things you have to consider while you develop your product prototype with an outsource service.
The Role And Importance Of Prototypes
"Developing an effective prototype in the early stages can provide many benefits in the product development process. Prototypes are known to be used as a crucial part of an iterative design process to realize and explore concepts. They can also help build product ideas into a manageable scope while working to establish the critical details and fully understand the design intent at the beginning of the product lifecycle. It also represents a powerful communication tool. A prototype is needed to help a project move forward with clear and actionable feedback on design, manufacturability, and other product considerations.
"On the other hand, fully functional prototypes can be used to test design iterations. This can help to reveal issues that need to be corrected before the design is finalized, reducing business risk and improving quality during the prototyping services. They could be made in several different versions, with low-cost materials used for form validation and fit check and a smaller number of test articles made with more expensive, production equivalent materials.
"Low-cost product prototypes often help designers and engineers verify product design, as well as their manufacturability and engineering, before running into issues during full production. High fidelity and cost-effective prototypes are essential for the engineer and designer to improve and optimize designs and ensure production goes as smoothly as possible. The sum of money spent on a prototype always pays its dividends later in the process.
Prototype Capabilities
"When it comes to working with an outside partner in developing your prototype, you need to take into account and consider multiple aspects regarding the outsource company you will choose. To ensure your prototype will be done to perfection, it’s essential to choose a highly skilled and capable prototyping partner. Instead of shipping different parts from different places and then assembling them in another location, it’s better if you choose a partner who can do everything in one place. Find a partner who’s committed to providing top quality rapid prototyping and low volume manufacturing services, including CNC machining, 3D printing, plastic injection molding, vacuum casting, etc.
"Working with a reliable company that can “do it all” guarantees your prototype security as well. If a lot of individuals or several companies get to see the design, there are chances of prototype design theft, and your competitors may get access to very private and confidential information. End-to-end prototyping capabilities of your sourcing partner should be a top-level matter to consider when considering outsourcing this service.
Experience And Versatility
"You should always go with a reputable company that’s been in the business for quite some time. You want an experienced team on your prototype project. Do your homework and do some research, how long the company has been in the industry, and make sure to check the reviews it received and the technology they use.
"Another factor to consider is the low-volume production versatility of the company. Low-volume products, in general, need a company that can handle small production well and effectively. Even when the development time is short, the outsourcers should ensure you meet your launch date and manufacturing of the prototype should always be on time.
Industry Familiarity
"Strive to pick a reliable partner that is familiar with what your industry manufacturers, or generally what it does. This will help the company have your interests at heart and work as hard as possible to get the best results with the prototype model. The experts in the outsourcing company should know the limitations and strong-holds of the materials, design, and the machines that have to be used in the process of creation.
"Having the same industry language is very important and beneficial as well. Without proper communication, you might not achieve the desired results and end up losing instead of gaining in the process.
Prototyping Technology
"As you already know, technology is always changing and advancing. Make sure that your partnering company is able to offer more complex, advanced, and high-quality designs. The best and most advanced technology mixed with expert knowledge of it will get you exactly where you want to go with the prototype. Working with the latest technology will enhance your product, make an upgrade in the development process, and get you to be more reputable in the industry."